|
BrianWhittaker.com |
|||||
| Home | Astronomy | Wallpaper | Noctilucent | Kilimanjaro | Contact |
|
Volcano |
|||||
| Brian's "Volcanic Aerosol Spotting" | |||||
 |
|||||
| Volcanic Aerosol: | (updated after significant large eruptions) | ||||
|
Volcanic ash can be visibly detected for weeks
after an eruption far away from the volcano that produced it. The
area immediately around the volcano and its dense ash plume
(Wiki) will
quickly be restricted for obvious reasons and most of the ash will
fall nearby. Much of the visible plume consists of water vapour, like
cloud, which will quickly dissipate. However smaller particles may be suspended for
thousands of miles, and others in the upper atmosphere will simply
float around the world for many weeks! Essentially there are two
main types of suspended volcanic material that will stay visible, fine "Tephra" Ash (small rock
or glass particles) and Sulphur Dioxide SO2
gas which forms Sulphate Aerosols. The ash can be visible for many
days looking similar to a thinning smog and stay suspended for weeks
contributing to beautiful sunsets. They vary in size and fall
quicker with weight, proportionate to size. The Sulphate Aerosols can also be
visible and look similar to high thin Cirrus Clouds for many days, but their
affects in the Stratosphere can persist for several years causing
cooling of the Earth's climate. Both spread and dissipate rather
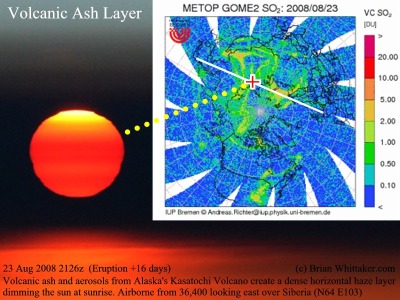
gradually travelling as clouds in the wind, like a giant swarm. Big eruptions are in the magnitude of one every couple of years. Astronauts filmed a spectacular eruption on 12 June 2009 from the International Space Station of Russia's Sarychev Peak (6MB QuickTime) (NASA) (Wiki) (map). This eruption punched well through the Tropopause into the Stratosphere where the particles travelled all around the world. Above is an image of its giant ash cloud from an airliner over central Canada. Notice the higher bluish SO2 cloud behind and above it. The SO2 created a high altitude Cirrus looking cloud that spread around the world and could easily be seen by jet traffic in the Atlantic Ocean and Europe as textured thin cloud with defined details many days later until it slowly dissipated. Eventually the lower ash also spread out and formed a marked haze layer at the tropopause everywhere in the northern hemisphere that could be easily seen on the Earth's limb in twilight. Weeks later, sunsets and sunrises were still showing an obviously exaggerated afterglow due to this upper ash layer as in the photo to the left from Los Angeles, USA. The volcanoes near the Russian Kamchatka Peninsula and Alaska's Aleutian Islands are remarkably active and affect the North Pacific airways each year. Further away in the Philippians in 1991 Mt. Pinatubo (Wiki) had an even larger eruption which also caused beautiful sunsets in North America and Europe. Even more spectacular was the legendary 1883 eruption of Krakatau (Wiki) where global visual and climatic effects lasted several years. Noctilucent Clouds, discussed below, were also first documented after Krakatau's extreme eruption. You may wish to also read about "1816 -the Year with out a Summer" [wiki] caused by 1815's Mount Tambora [wiki] eruption . Specialized scientific satellites (SO2 Map) (TOMS) can track associated Sulfur Dioxide clouds until they dissipate, but volcanic ash clouds are not as detectable. In addition, please note that aircraft weather radar does NOT detect volcanic ash. Iceland's 2010 eruption of Mt. Eyjafjallajokull (Wiki), (NASA), that closed European airspace with unprecedented economic repercussions, showed us that the technology is still being developed. It must be noted that, until further defined, any amount of ash is considered detrimental to aircraft and must be avoided. [CAA Info], [UK MetOffice ash Charts], [UK MetOffice aviation], [maps] There are many active volcanoes around the world with continuous local ash and gas releases. Most smoldering volcanoes leave a thin local haze (Wiki) which stays at relatively low altitudes and dissipate quickly. Perhaps you have seen volcanic aerosols before and not realized it? For example, one volcano in Japan (Mt Asama), (map) often fills the sky over Tokyo (130km SE) with a slight haze that most aviators falsely assume is pollution. Note that the vast majority of volcanic eruptions are simply low-level local events. Russia's Sarychev Peak (NASA), (Wiki) Volcano Krakatau 1883 (Wiki) Afterglow from Sarychev at LAX. (Wiki) |
|||||
 |
A volcanic eruption is a pretty dramatic event and must be avoided. For this reason, the world spends considerable resources monitoring volcanoes and distributing the information globally for all. Although heavy debris falls near the volcano, clouds of ash and gas may travel considerable distances and stay aloft for many days or longer. There is a lot of water vapor in a volcanic plume that will look dramatic but evaporate into the air, like a dispersing cloud. Sulfur Dioxide gases may rise high into the Stratosphere and circle the globe several times or persist for weeks appearing like a very high thin cirrus layer. This is harmless to aviation, but unfortunately has an affect on global cooling. Other gases containing sulfur may spread a layer of "rotten egg" smell that may be experienced considerable distances away. The sulfur smell is so strong that only a harmless amount may be significantly noticed by all who pass through this layer. Although most ash will fall near the volcano there is always an immediate Restricted Area created by the authorities to protect the airspace for the obvious reasons. Pilots are forever vigil in the unlikely event that they could be the first to discover a new unknown eruption. Other finer ash and aerosols can travel for thousands of miles and stay in a huge cloud maintaining a random altitude. It can do this because the ash is so fine that it is suspended in the air and other forces become more significant then gravity. Frankly, it is slowly becoming a less concentrated aerosol particle cloud and is no longer a substantial threat to aviation. Yes, in stronger doses it certainly can corrode an aircraft's paint or windscreen, or create addition maintenance procedures, but these isolated cosmetic cost risks simply have to be absorbed and balanced with the fare, like a strong headwind's affect on fuel costs for a given flight. At what point the concentration and particle size become insignificant is still being discussed between aircraft and engine manufacturers, however at what point ash becomes a risk is well understood and it is always avoided. There is always some amount of volcanic aerosols suspended in the atmosphere, the only variable is how much. It can last for years and usually spreads inbetween and beyond individual eruptions. |
||||
|
Historic:
|
I have only been a serious "Aerosol Spotter" for about 12 years. I think you need to be significantly high and cruise long distances to see and fully appreciate the differences in the atmosphere. Quite often the affects are very subtle and essentially unnoticeable but occasionally there is a noticeable change. Historic Volcanoes like Krakatau in 18___ would have been very interesting to observe had airplanes been invented yet. Other volcanoes like Mt Paotitoo in the Philippines were noticed by many pilots all over the world for years. Astronauts also recorded atmospheric aerosols from space. Despite watching subtle changes for years, my first observational break-through wasn't until 2008. | ||||
| Mt Kasatochi 2008 | eTo pti | ||||
|
|||||
| Sarychev Peak 2009 | |||||
|
|||||
| Iceland 2010 | |||||
|
|||||
| Iceland 2011 | |||||
|
|||||

|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
 Debris 16 July 2009 (+23 days) Victoria, BC, Canada PHOTO 680 |
|
|
|